What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange is the exchange of information between trading entities in electronic format. There are different internationally accepted EDI formats in use today, based on the industry and geography using it and these have evolved.
Before companies adopted Electronic Data Interchange, they managed a large part of their regular operations through manual methods that include paperwork, faxes, and emails. Electronic Data Interchange as technology has helped companies exchange transaction information by negating reliance on massive paperwork and human intervention, thereby saving processing cost and time. With EDI, the trading partners agree on a format, and exchange information in the structure, the format defines. Their respective destination systems, receive the information and update the applications that are part of the EDI ecosystem.
Structure of an Electronic Data Interchange
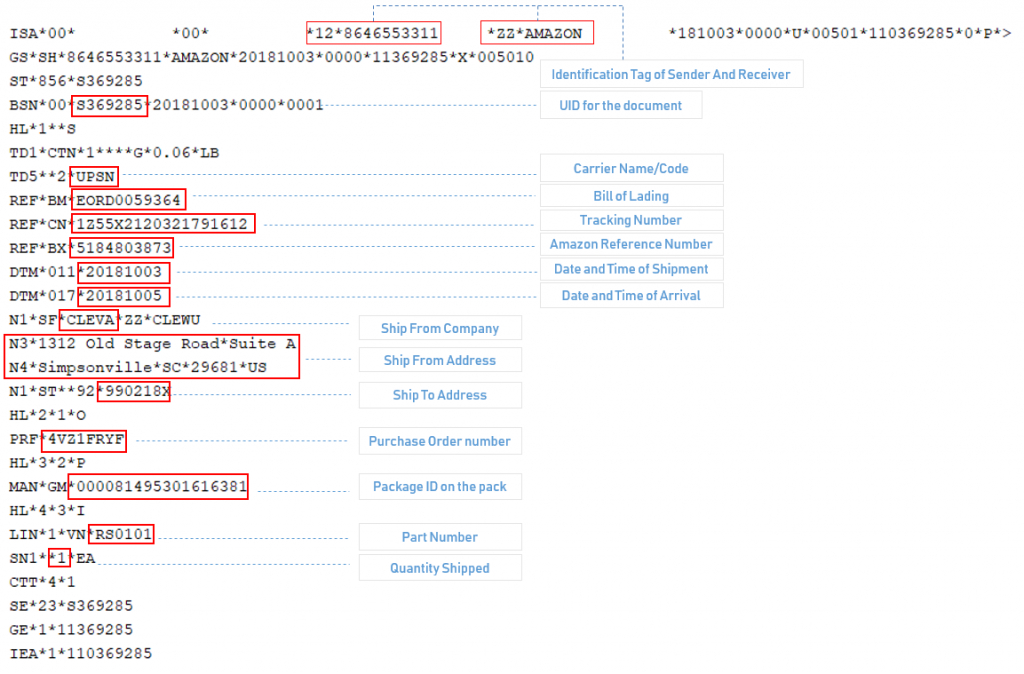
Given above is a sample 856’s structure. The EDI 856 transaction set is called an Advance Shipment Notification or ASN. It belongs to the ANSI X12 EDI standard. It is sent by the entity that is shipping the goods to the entity that will receive the shipment. It provides details of the shipment. As the name denotes, it is sent prior to the shipment’s arrival at the receiver’s facility.
Highlighted in red are some of the critical information pertaining to a shipment. Example, who is shipping to whom, what and how much is shipped, mode of transport, shipment date and time, arrival date and time, package details etc. Every time a shipment is made, the details are sent in the same structure reducing chances for errors and loss of information.
The trading entities who have agreed to follow this standard must adhere to the information structure defined by the standard.
What does an EDI set up constitute?
- Connection protocol — A connection is established between the trading entities through a secure and reliable network for transfer of files.
- EDI Standard — The trading parties agree upon an Electronic Data Interchange format, that they would use to exchange transaction data. The format defines how data should be presented. This brings uniformity and coherence to how information is read and processed.
- EDI Software — The software converts EDIs into electronic format. It receives and generates EDIs with every business action. The software is designed or customized to receive, read, process and generate EDIs and update systems according to the EDI practices of the trading entities.
- EDI and applications — Every EDI received and generated is not merely the transfer of data but implies the completion or initiation of business action. The Electronic Data Interchange software is often connected to multiple other systems that manage demand, inventory, orders, receipts, and invoices, capturing business progress.
Reach out to the author of this blog at hello@byteally.com, and feel free to mail your comments or suggestions.
